What Is a Vision System? What does it include?
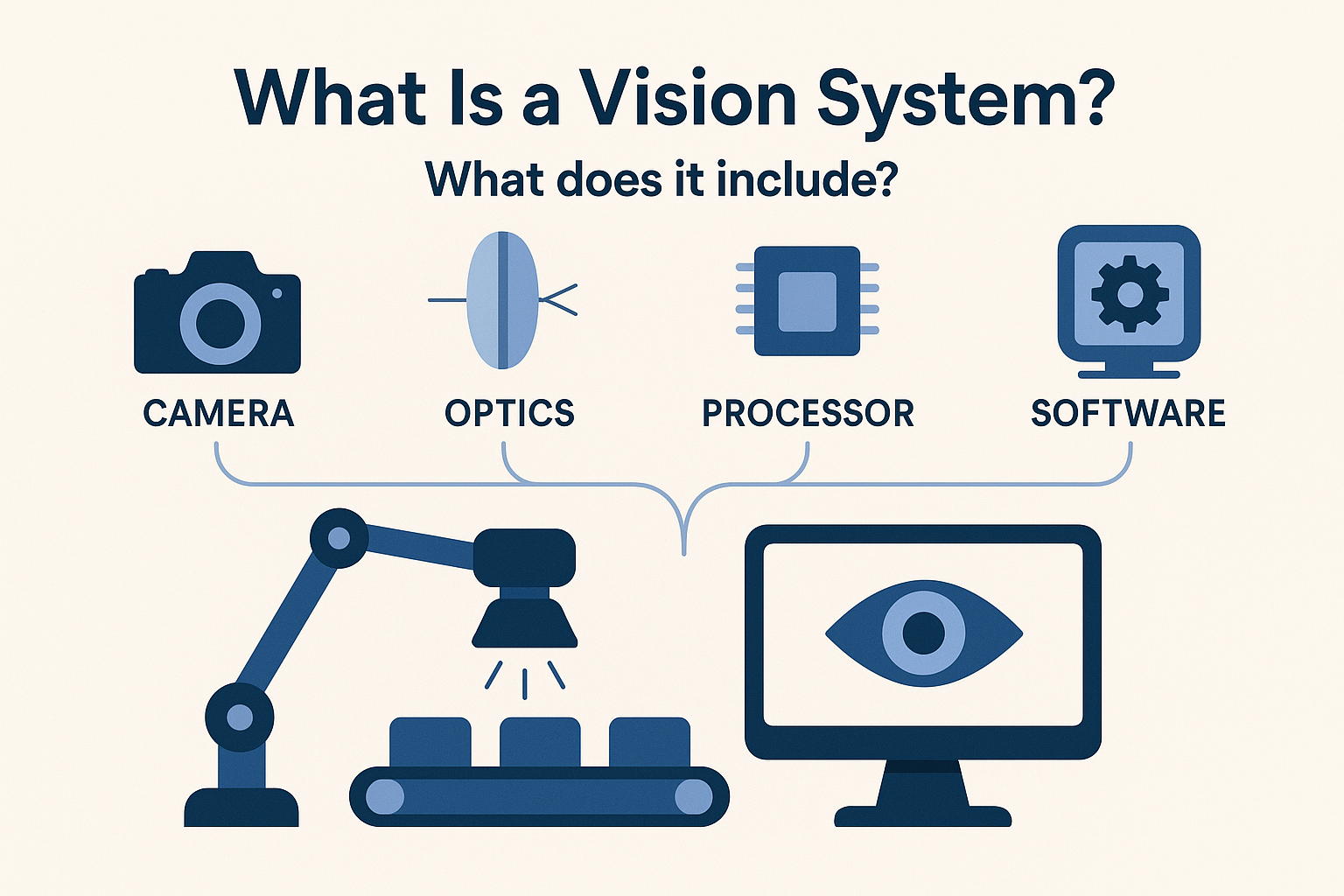
Machine vision systems are vital in today’s fast-changing industries. They automate inspections, improve quality control, and boost efficiency. A vision system combines cameras, sensors, and smart software. This setup allows machines to “see” and make decisions using visual information. But what exactly is a vision system, and what components does it include?
Understanding 2D vs 3D vision is crucial for businesses selecting the right automation solution. Both methods aid visual inspection. However, they differ in depth perception, accuracy, and uses.
This guide covers what a vision system is. It details its main parts and shows how it helps various industries.
What is a vision system?
A vision system combines hardware and software. It captures, analyzes, and interprets visual data. This helps in making decisions or controlling processes automatically. These systems mimic human vision but with much greater speed and precision.
In manufacturing, vision systems do many things. They find defects in products, measure dimensions, read barcodes, and guide robotic arms. In healthcare, they assist in medical imaging and diagnostics.
Key Components of a Vision System:
A typical vision system includes:
1. Camera or sensor
The camera is the “eye” of the system, capturing images of the object or scene. Cameras can be:
- 2D Cameras: They take flat images. They work well for barcode reading, label inspection, and finding surface defects.
- 3D Cameras: They capture depth information. This helps with tasks like object recognition, bin picking, and measuring volume.
2. Lighting:
Proper illumination is crucial for high-quality image capture. Pick lighting techniques such as backlighting, diffuse lighting, or directional lighting to fit your needs. Each method highlights different features.
3. Lens:
The lens focuses light onto the camera sensor, ensuring clear and undistorted images.
4. Image Processing Software:
This is the brain of the system. It looks at images and finds patterns. It also measures sizes and sends signals to other systems, like robotic arms.
5. Controller or Processor:
This unit runs the whole system. It processes visual data and carries out actions using algorithms.
Applications of Vision Systems:
Vision systems are used in various industries.
- Manufacturing: quality inspection, sorting, and defect detection.
- Automotive: Guiding robots in assembling car parts.
- Food Industry: Checking packaging and labeling accuracy.
- Healthcare: Assisting in precise surgeries and diagnostics.
- Logistics: Tracking parcels and automating warehouse operations.
2D vs. 3D Vision: Which is Better for Your Needs?
When picking a vision system, it’s important to know the difference between 2D vision vs 3D vision.
- 2D Vision Systems is great for flat image tasks. They work well for scanning QR codes and spotting surface scratches.
- 3D Vision Systems work well for tasks that require depth perception. They can measure how tall objects are. They also guide robotic arms to pick items. Plus, they can manage oddly shaped objects.
For a detailed comparison of these two approaches, check out 2D vision vs. 3D vision.
Why Choose Meaxpert for Vision Solutions?
Choosing the right partner for your vision system is crucial. Meaxpert focuses on providing advanced 2D and 3D machine vision solutions. We tailor our services to meet your industry needs. Meaxpert is dedicated to innovation and precision. They provide smooth integration of vision systems for automation and quality control.
Final Thoughts:
A vision system is not just a camera. It’s a smart tool that helps machines analyze and respond to what they see. Choosing a 2D or 3D vision system depends on your needs and process complexity.
Industries can stay ahead in automation by using the expertise of top providers like Meaxpert. This helps them achieve better accuracy, efficiency, and quality.