How Quality Management System Software Transforms Traditional QMS Manual Processes
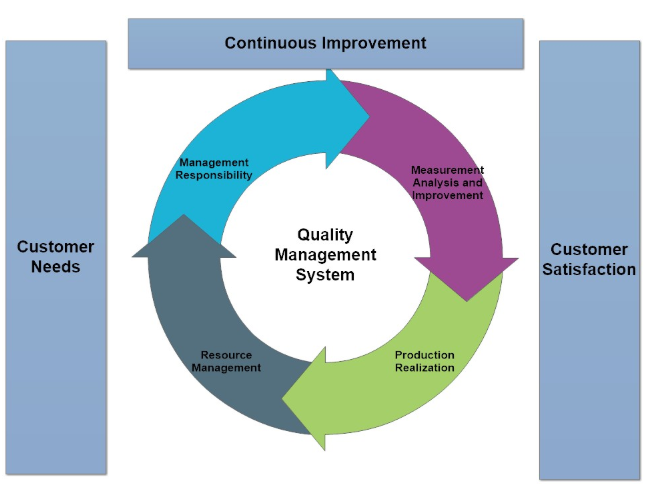
With today’s business world, the pursuit of excellence in product quality, operational efficiency, and compliance is higher than ever. In order to sustain themselves amidst such turbulence, organizations must leverage technology’s revolutionary power to transform their Quality Management Systems (QMS). Technology is not only an enabler but a driver of forces of QMS transformation, revolutionizing the way organizations approach quality control, process improvement, and risk management. QMS has undergone tremendous transformation, starting from the primitive paper-based system to the highly advanced data-driven system that defines the modern day. With the continuing improvement of technology, technology-facilitated modernization of QMS has become an important element in maintaining competitiveness in the market. This white paper addresses the essential role that technology plays in modernize QMS, unveiling the benefits, issues, and emerging trends that will shape the quality management landscape in the next few years. As we embark on this journey of technology and quality convergence, we will discover how organizations can utilize the potential of innovation to achieve levels of quality, compliance, and competitiveness previously unknown.
Role of Quality Management System With Technology
The Quality Management Systems (QMS) that are technologically advanced offer various advantages to organizations across different industries. With companies anticipating enhancing product quality, streamlining processes, and competing within a rapidly evolving market environment, embracing technology in QMS has become imperative. In the succeeding section, most of the benefits that the application of technology in QMS brings about are explained.
- EFFICIENCY AND COST SAVINGS- New QMS technologies eliminate redundant work and reduce the need for manual intervention. This streamlines processes, reduces errors, and maximizes resource utilization. Companies can thus operate more efficiently, reduce operating expenses, and free resources to be allocated to core initiatives.
- ENHANCED COMPLIANCE AND RISK MANAGEMENT- With regulatory requirements changing continuously, compliance can be a time-consuming and complex task. Technology-enabled quality management software solutions provide real-time compliance monitoring, documentation, and reporting. This keeps the organization compliant with regulatory requirements all the time, reducing the risk of fines and legal problems.
- REAL-TIME VISIBILITY AND CONTROL- Integration of IoT and real-time monitoring systems with QMS provides unparalleled visibility into supply chains and production processes. Real-time visibility in this way enables organizations to observe and correct quality defects as they emerge, thus preventing disruption and defects.
- DATA-DRIVEN DECISION-MAKING- Technology supports organizations to harness the power of data for data-driven decision-making. Analytical and AI-driven QMS software makes data analysis possible at scale. Organizations can make data-driven decisions to enhance processes and drive continuous improvement through actionable insights from quality data.
- ENHANCED CUSTOMER SATISFACTION– Regular service and quality products are key drivers of customer satisfaction. Modern QMS guarantees that products will satisfy or exceed customer expectations, fostering brand loyalty, word of mouth, and repeat purchases.
- SUPPLY CHAIN OPTIMIZATION- Technology-driven QMS solutions spread their advantages beyond organizational confines. They deliver quality information about raw materials, components, and finished goods along the supply chain. This transparency enables organizations to make well-informed decisions, reduce supply chain disruptions, and harmonize with suppliers
- COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE- Firms that implement technology so that their QMS will be computerized enjoy a competitive advantage. They can deliver goods to the market faster, provide better service to their customers, and maintain a quality and reliability image.
- EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT- Modern QMS can include simple and easy-to-use interfaces and tools that enable workers to take an active part in quality management. This instils a quality culture in the organization, and employees are encouraged to identify and report defects, leading to continuous improvement.
- CLOUD-BASED QMS- Cloud computing enabled organizations to host their QMS centrally so that they can be accessed by global stakeholders. Cloud-based QMS solutions provide scalability, flexibility, and real-time collaboration features and are thus a hallmark of modern quality management.
KEY CHALLENGES IN ADOPTING TECHNOLOGY FOR QMS
Even though QMS with technology has various benefits, organizations must overcome some challenges in adopting technology for their quality management systems. Recognizing these challenges, selecting the right QMS vendors who would collaborate with your staff easily and cheaply and coming up with solutions to address them is the key to a successful QMS modernization program. The subsequent section presents the most significant challenges of applying technology for QMS modernization.
RESISTANCE TO CHANGE- Resistance to change among employees and stakeholders is one of the biggest challenges of implementing technology for QMS modernization. People are accustomed to the old processes and are less accepting of new technologies and methods. Proper change management techniques, open communication, and training and empowerment of employees are required to overcome this resistance.
DATA SECURITY AND PRIVACY CONCERNS- With increased reliance on digital technologies, data security and privacy concerns become all the more significant. Measures to ensure sensitive quality data is protected from cyber attacks and compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) are not simple but inevitable. Organizations must implement top-of-the-line cybersecurity software and data encryption to safeguard quality data.
INTEGRATION COMPLEXITY- QMS today often involves connecting multiple software products and systems, including ERP applications, IoT sensors, and analytics tools. Smooth integration may be a challenge and require specialized technical expertise. Silos of information and incompatibility issues may make the QMS software irrelevant.
HIGH COSTS OF IMPLEMENTATION- While this factor can be a zero factor if Quality persons and vendor selectors are strictly particular in vendor selection based on value and cost, otherwise, Implementation of cutting-edge QMS technologies often comes at high initial costs, i.e., software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and training. Small organizations, in particular, will lack the capability to invest the necessary funds in an integrated QMS modernization initiative. Vendor selection, budgeting, and cost-benefit analysis are extremely critical to render the investment feasible.
SHORTAGE OF QUALIFIED WORKERS- Effective leveraging of advanced QMS technology requires a skilled workforce. Companies may face challenges in retaining and attracting employees with the necessary skills in data analytics, AI, IoT, and cybersecurity. In-process training and upskilling are necessities to bridge this skills gap.
DATA QUALITY AND ACCURACY- Reliability and accuracy of data are the essence of QMS. Technology-enabled QMS relies on data input from varied sources. Inaccurate or incomplete data could lead to erroneous decisions and quality issues. Ensuring data quality through cleansing and validating processes is essential.
CHANGE MANAGEMENT- Implementing technology-enabled QMS is more than simply installing new software. It must be accompanied by a cultural shift within the organization. Without leadership support and change resistance, projects will flounder. Effective change management practices, including executive sponsorship and employee engagement, are crucial for success.
SCALABILITY AND FUTUREPROOFING- Technology evolves rapidly, and QMS solutions must be scalable and future-proof to maintain the capacity to support future advancements. Organizations can struggle to maintain their QMS as being relevant and efficient in the long term. This requires a proactive strategy towards technology refreshes and future-proofing programs.
Conclusion
In summary, the transformation of QMS by technology is multi-fold, including
improved product quality, cost savings, improved compliance, and the potential to make decisions based on data. Also, it enables agility, enhances customer satisfaction, and positions organisations for long-term success and sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, organizations that embrace these advancements in their QMS will remain competitive and adaptive to shifting business landscapes. Dispelling change resistance, dealing with intricate integrations, data protection, and regulation complexities are a few of the most significant challenges. Successful QMS modernization requires a strategic approach, clear planning, and a commitment to addressing. read more