Rapid prototyping technology can shorten product development cycles by 40%, helping UK SMEs gain a competitive edge in the market
Introduction
The current pace of the market means that, in the UK, SME businesses are effectively missing the boat on vital opportunities due to extended timescales for the development of their products. The reality is that the use of traditional approaches for prototyping is, on top of being very expensive, also fraught with high risk. The problem fundamentally relates to the inability to adapt to traditional manufacturing processes, the inefficiencies associated with the lack of effective collaboration, and the absence of proper advanced manufacturing technology to aid quick validation, making the concept to physical part production cycle a long one and unsure.
This article will explain the effective use of advanced metal rapid prototyping and professional rapid prototyping services and the impact on the current rapidly paced market by creating a nimble loop for developing products, substantially reducing the timelines and impacting success ratios with industry automation and advanced technology solutions. The subsequent sections will describe the key strategies and technology to accomplish this.
What Is the Impact of Rapid Prototyping Technology on the Contemporary Process of Developing Products?
“Model making” has, therefore, moved from being relegated to rapid prototyping to becoming an important risk management and quick decision-making exercise. Its objective is to facilitate rapid iteration, wherein flaws in design can be pointed out and rectified in time, thereby avoiding expensive changes down the line. According to The International Society for Automation (ISA), digital threads, which link several stages of product development, can lead to time reductions of up to 50%. This clearly identifies the spirit of rapid prototyping, wherein an iterative design involving design, simulation, and verification occurs.
The Strategic Significance of an Agile feedback loop
The classic linear development process (design, tooling, test, and then modify) is being converted into an agile, closed-loop process. New methods involve metal rapid prototyping techniques that incorporate a closed-loop process. Designs are analyzed by CAE software, and the information is transmitted at the same time to rapid prototyping services, creating functional parts that are then physically tested. This process has greatly changed the way development was done in the past because it transformed the linear process into an agile one.
Combining Services for CAD, CAE, and Rapid Prototyping
The beauty of this solution is that there is seamless integration of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE), and rapid manufacturing. These four aspects form an integrated digital process that guarantees integrity of data from the digital model all the way through to the physical object that is created. All this is important for high-quality rapid iteration, and indeed “what you design is what you get” is now a fact, and this goes from digital design all the way through to a prototype.
The Importance of Metal Rapid Prototyping
Metal rapid prototyping has great strategic value for its capability to produce functional and robust parts that have properties very close to the final production parts. This form of prototyping enables concept testing through form and function.
- Comprehensive Design Validation
Designs can be tested for functionality, thermal resistance, and assembly compatibility, allowing engineers to validate a design before investing resources into production tooling.
- Informed Stakeholder Engagement
Physical prototypes are useful tools for gaining approvals from management, attracting funding from investors, as well as gaining informed customer insights, reducing decision-making pathways.
- Encouraging Innovation
It enables and empowers teams to be involved in more innovation and complex design works which might be considered to be risky with traditional methods. Strategic use of metal rapid prototyping is at the core of agile manufacturing.
What Role Does Precision Engineering Play in Ensuring Prototype Functionality and Reliability?
The main purpose of a functional prototype is to model the actual performance of the finished product. For this reason, high-quality prototype machined parts are essential for a thorough test. The principles that work together for a well-engineered product concerning precision mechanics include tight tolerance requirements, high surface finish quality, and geometric precision. For example, a fluid valve prototype with carefully machined internal passages will yield reliable results for flow resistance, or a transmission part that has tight tolerance requirements for a proper assembly.
Technologies that involve CNC machining rapid prototyping are of utmost importance for ensuring that this level of accuracy is achieved. Modern CNC technology has the capability of cutting even complex metal components with a level of accuracy that is measurable only on a micron level, thus satisfying even the most rigorous testing demands for functionality and reliability. In sectors that demand a certain level of reliability, such as in cars and airplanes, it is important that firms work with companies that hold international quality certification, for example, IATF 16949 is critical.
How does industrial automation and 3D printing further increase the rapid prototyping process?
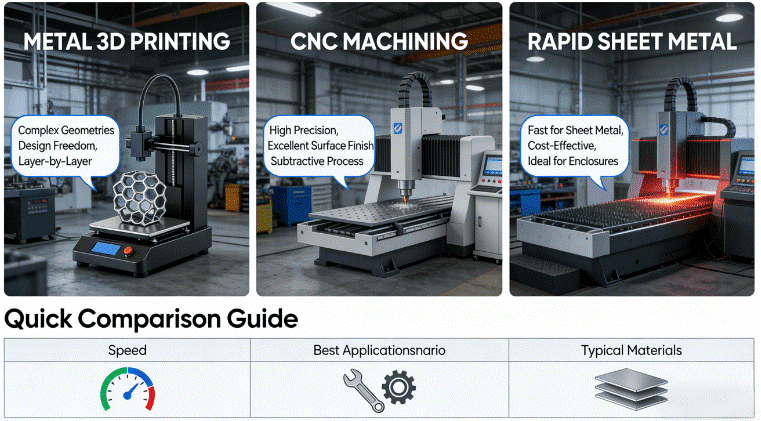
Figure 2: Choosing the Right Tool: A Comparative Overview of Key Rapid Prototyping Technologies for Speed and Application.
Automation in Industry is one of the most important enablers in the next leap in prototyping speed. Automated processes, starting from CAM programming and down to machine operation, facilitate prototyping operations in a non-stop, near 24/7 mode. In CNC machining rapid prototyping, automation by way of automated tool changers and pallet changers enables machines to work unceasingly, which shortens prototyping time significantly. Moreover, metal 3d printing rapid prototyping is one of the most advanced levels of automation. After preparing the digital file, the prototyping procedure can run on its own, with its capability to produce complex shapes in one single operation—the production of internal cooling holes and lattice structures.
The technology to be used will depend on the requirements of speed, material, and complexity involved in the application. This is compared to other technologies as shown in the table below:
| Technology | Typical Applications | Relative Speed Advantage | Key Applicable Scenarios |
| CNC Machining Rapid Prototyping | High-precision functional parts, assembly tests | Very fast for simple or medium-complexity parts | Prototypes requiring near-production performance, high accuracy, and excellent surface finish |
| Metal 3D Printing Rapid Prototyping | Complex lightweight structures, internal channels, unified assemblies | Significant advantage for highly complex geometries | Topology-optimized structures, parts impossible to make traditionally, small-batch customizations |
| Rapid sheet metal prototyping | Enclosures, brackets, chassis, sheet metal assemblies | Fast and cost-effective for sheet metal components | Validation of electronic housings, metal covers, and various sheet metal structures |
As per guidelines provided by certain organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), one of the benefits offered by automation is the elimination of human error, ensuring consistency in production.This is to ensure that each prototype, whether from the first or the hundredth production, is of the same high standard.
How Should SMEs Evaluate and Manage the True Cost of Metal Prototyping?
When assessing metal prototyping cost, it is crucial to go beyond thinking in terms of “per-part cost” and focus on a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) approach. In other words, there are cost considerations which are both visible and “invisible,” and which might be described in terms such as time to market, opportunity cost, and risk of design changes at a later stage. There are clearly scenarios where taking advantage of higher speed and higher quality prototyping results in net cost savings.
Cost Optimization in Design
Efficient cost control starts during the design process. A service-based intervention through Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is the best way to address cost concerns. Consultation with the engineers at a rapid prototyping services firm for a DFM assessment may help in optimizing the design in a way that avoids material waste and machining, and speeds up the build process. A marginal change during the initial design stage can significantly impact the end product cost.
The Business Supply Chain Perspective
Adding professional prototype development services into the business supply chain early on has a major cost savings potential.
- Minimizing Late Stage Changes
It can be afforded that the cost of change in design identified in the prototyping phase is far lower than in the case of production tool development.
- Faster Time-to-Market
Faster iteration speeds up the product launch process, which allows an organization to tap the market shares before rivals do, thus achieving more income compared to the cost put into prototyping.
- Minimizing Inventories and Logistics Expenses
On-demand prototyping will reduce the inventory level of raw materials and finished components, and an effective supply chain will optimize logistics.
Leveraging Professional Engineering Solutions
It is important to partner with a supplier that provides complete engineering solutions with clear costing. The aim, therefore, is not only to identify a supplier with lower costs but to identify a supplier that can assist with improving the development process, and this is what professional rapid prototyping services essentially provide.
How to Choose a Prototyping Partner for a More Resilient Supply Chain?
Choosing the appropriate prototyping partner can have strategic implications that can directly influence the robustness and responsiveness of the company’s business supply chain. The appropriate prototyping partner will serve as an extension of the internal staff and will deliver additional expertise. An appropriate decision-making framework will have to be applied in ranking the possible partners against key criteria.
Technical competence and versatility are a starting point. The partner needs to be skilled in a variety of technologies (CNC machining, 3D printing, sheet metalworking) to be able to offer expert inputs on which is the most suited for each development stage. Quality certifications like ISO 9001 and, for industries with high standards such as aerospace, AS9100D are absolutely essential to show focus on quality and quality by association.
For instance, selecting a supplier such as JS Precision with aerospace industry quality accreditation AS9100D guarantees the delivery of prototypes with exemplary quality. In addition, efficient and uninterrupted communication and engineering solutions through materials are essential for successful execution. Finally, to future-proof a business supply chain, there is also a need for scalability to offer a smooth progression towards volume production starting with prototyping.
Conclusion
The integration of cutting edge rapid prototyping technology into the product development plan is now not an option, but an essential need in the case of UK SMEs. This is the key to maintaining agility in a competitive world. Through the adoption of metal rapid prototyping services, precision engineering, and automation, and through collaboration with experts who deliver complete engineering solutions, a superhighway from concept to product can be built.
Engage with professional rapid prototyping services today to bring your ideas to the market as market-ready products and initiate your first step towards leadership.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert who has over a decade of experience working with CNC machining, rapid prototyping, and additive manufacturing to help companies around the world optimize their product development process, from concept to production.
FAQs
Q: How do the materials used for RP and traditional prototype manufacturing compare?
A: Rapid prototyping emphasizes quick iteration and functional verification, extensively leveraging digital/automated tech, while classical prototyping is tool-based and has slow cycles, mainly verification testing. The latter is more appropriate for current agile development requirements.
Q: Is it possible to produce high-strength functional prototypes by metal 3D printing?
A: Yes, metal 3D printing processes such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) can create a dense material with properties close to that of a forged material, making them very apt for the field of testing.
Q: What are the important factors that influence metal rapid prototyping lead time?
A: Key considerations include part complexity, machining process choice (CNC machining may be quicker for simpler parts), post-process requirements, and the vendor’s production schedule.
Q: How might the unit cost of small batch prototype production be reduced?
A: Alternatively, optimizing designs for minimizing material wastage and machining time, identifying the most feasible process that is cost-effective, and working with suppliers that have better prices, like suppliers who have lean production processes, can be helpful in cutting costs.
Q: What factors are involved in scaling a prototype into a product suitable for large-scale manufacturing?
A: It is important that the design for a prototype has given due consideration to manufacturability, partner with a company that has the skill set to make a smooth transition from a prototype to a product, and make early supply chain decisions.